Master-slave replication
The master serves reads and writes, replicating writes to one or more slaves, which serve only reads. Slaves can also replicate to additional slaves in a tree-like fashion. If the master goes offline, the system can continue to operate in read-only mode until a slave is promoted to a master or a new master is provisioned.
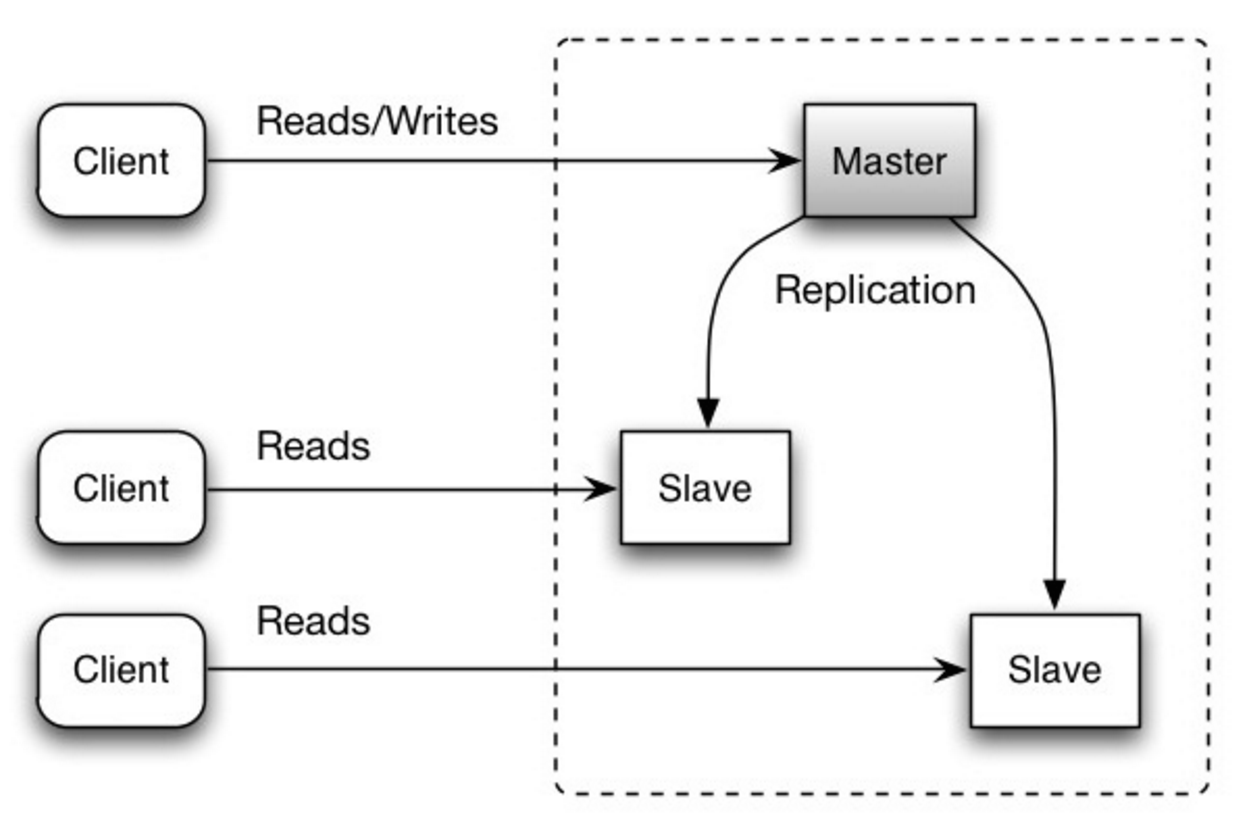
Source: Scalability, availability, stability, patterns
Disadvantage(s): master-slave replication
- Additional logic is needed to promote a slave to a master.
- See Disadvantage(s): replication for points related to both master-slave and master-master.